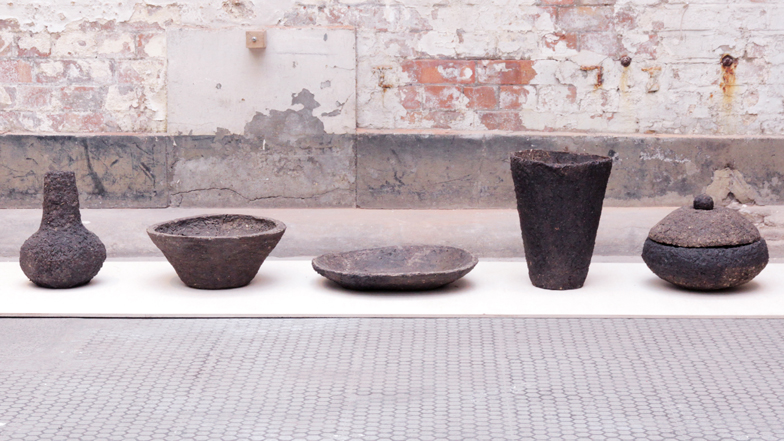
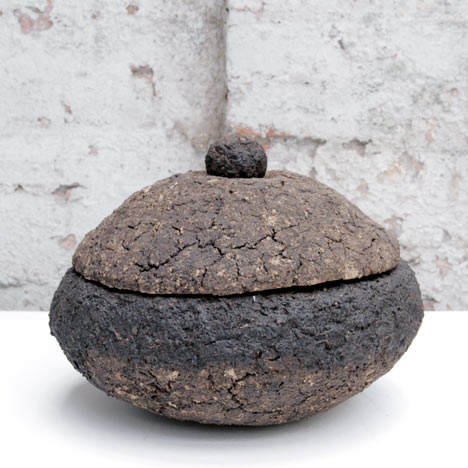
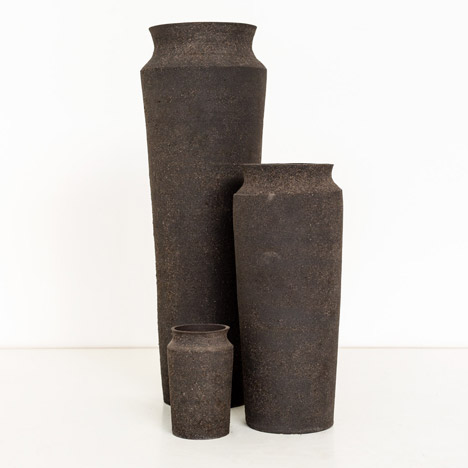
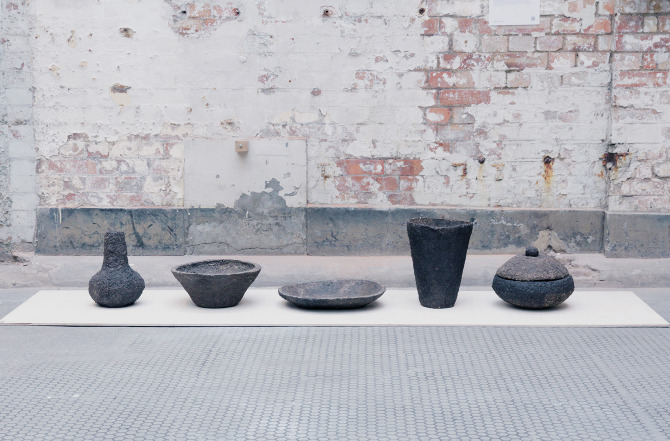
While earth, the material and technology that comprises the ground beneath our feet, is considered the most earth-friendly of all materials, it is also a material whose properties can be polluted by man-made and natural disasters. Artists have addressed this by fashioning objects made from the polluted ground.
Swedish artist Hilda Hellström created food storage jars made of radioactive earth from the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster area in Japan. To do so, she contacted the last person still living inside the evacuation zone, Naoto Matsumura, and collected soil from his rice fields that can’t be farmed due to contamination.
Similarly, design studio Unknown Fields Division has used mud from a toxic lake in Inner Mongolia to create a set of three Ming-style vases.
The London studio, headed up by Kate Davies and Liam Young, collaborated with ceramicist Kevin Callaghan to form the three radioactive vases from the toxic waste generated during the production of electronic devices like smartphones and laptops, as well as a short film.
“Rare earth minerals are some of the fundamental ingredients in contemporary electronics,” said Young. “For example, a smartphone has eight different rare earths in it. Everything from the material used in its memory to the red-coloured pixels of its screen and the polish used on its glass.”