EarthUSA 2011 will be Sep 30, Oct 1 and 2. Location will be at the National Hispanic Cultural Center in Albuquerque, New Mexico, USA.
This is the Sixth International Earthbuillding Conference sponsored by the Adobe Association of the Southwest and Northern New Mexico College. The National Hispanic Cultural Center and Adobe in Action will also be sponsors. The Adobe Association of the Southwest is expected to turn itself into Adobe USA.
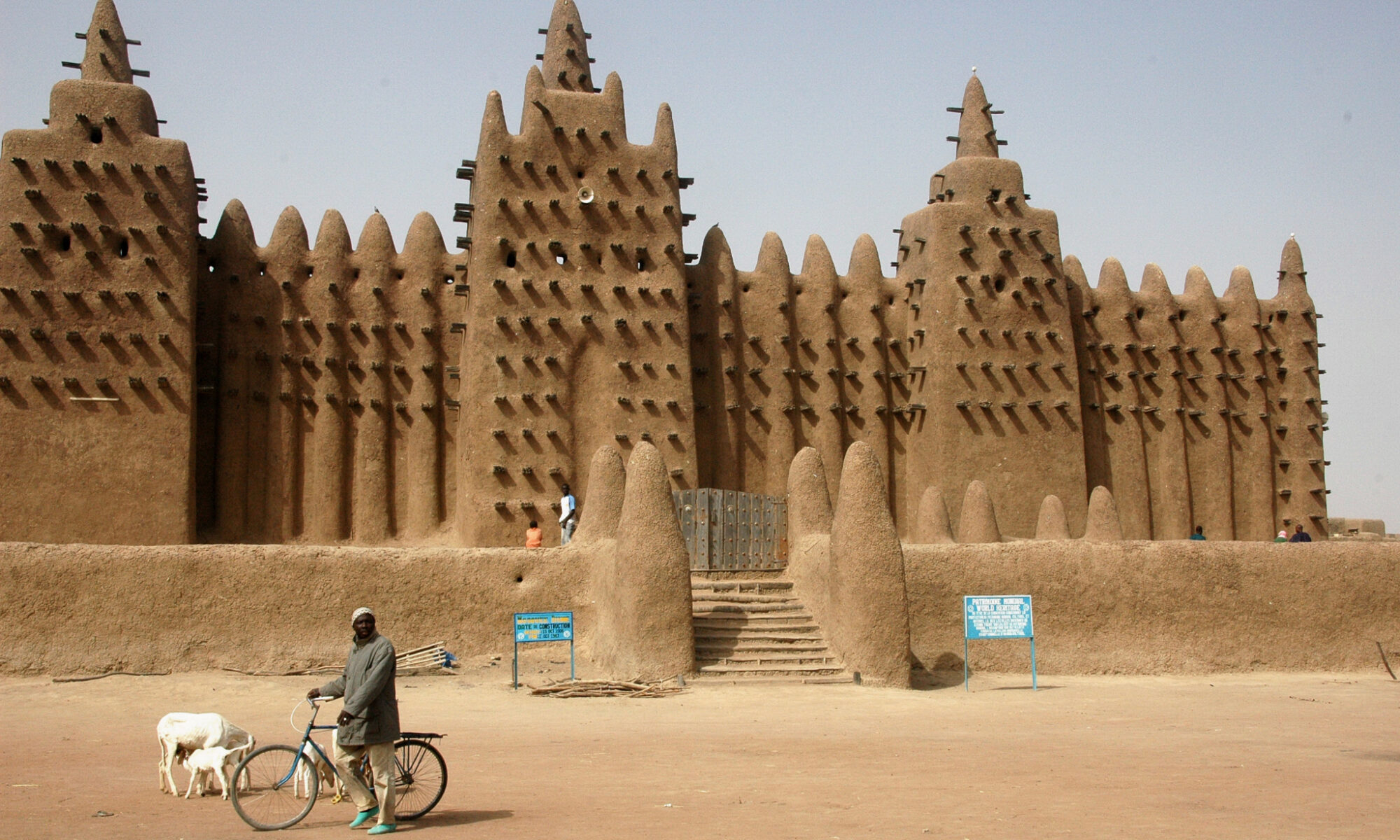
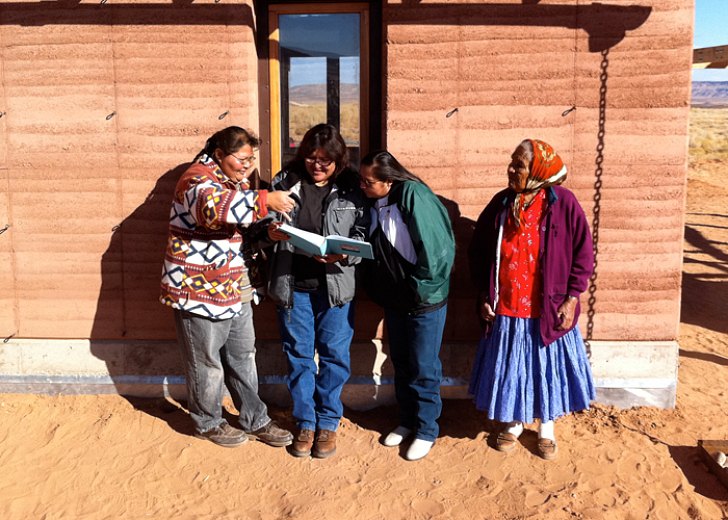
EarthUSA 2011 indicates a wider field of interest than previous conferences and will include adobe, rammed earth, compressed earth block: CEB, and monolithic adobe: cob. Any material or method that uses clay to bind it together is considered.
Calendar:
May 3: Abstracts due
Jun 3: Acceptance notifications
Aug 5: Full Papers due
Sep 9: Proceedings go to press
Sep 30, Oct 1: Conference and Trade Fair
Oct 2: Tour
Oct 3 -7: Classes, Workshops
Oct 1 – 9: Albuquerque International Balloon Fiesta
Categories/Themes:
1. Contemporary earthen architecture, construction and engineering
2. Historical buildings, farms, villages and cities including cultural connotations
3. Conservation, Preservation, Replication, Remodeling, Modernizing, Re-purposing
4. The role of earthen materials in heating, cooling, sustainable, ecological, renewable and green design
5. Codes, norms, building methods, material science, seismic considerations
6. Earthbuilding education and technology transfer
7. Marketing strategies for earthen materials in the modern world
Conference Languages:
Spanish and English
Papers will be printed in the Conference Proceedings in the language received. Papers received with translations will be printed in both languages PowerPoint presentations are encouraged to be labeled in both languages
Costs:
The Conference Registration will cost $185 USD with reduction for students. Authors and presenters also pay the registration fee. EarthUSA 2011 is a small conference with few financial resources. A one-day tour will be available Sunday for local earthbuilding sites the cost to be determined. Four and five-day courses and workshops October 3 through 7 are being planned and will include basic adobe construction; rammed earth construction; and arch,vault and dome construction.
Submit your abstract as an e-mail attachment in .DOC format no later than May 3, 2011. Please address your e-mail to: Quentin Wilson, Speakers Committee: earthusa.org@gmail.com
For more information and to download the abstract template visit: www.earthusa.org