
MYOO.com, the online home for fresh and compelling content that’s geared towards kickstarting a smarter 2.0 way of living, features a discussion with Earth Architecture author, Ronald Rael.

Architecture, Art, Design, and Culture using of mud, clay, soil, dirt & dust.

MYOO.com, the online home for fresh and compelling content that’s geared towards kickstarting a smarter 2.0 way of living, features a discussion with Earth Architecture author, Ronald Rael.

Photography: ©Harrison Photography
Saint Bartholomew’s Chapel, designed by Kevin deFreitas Architects, was constructed to replace a very small and intimate historic chapel that was ravaged by wildfires in 2007. From that fire, only the original adobe bell tower survived, which became the anchor element in the redesign planning.

Photography: ©Harrison Photography
The new design was conceived to reverently knit together “past” and comfortable traditions, while acknowledging and offering something relevant to current and future generations. Thus, emulating or recreating the past literally was not a project goal. Drawing from a limitless well of Native American and Catholic symbols and metaphors, design elements in plan, section, and elevation were conceived to reference and infuse meaning into the chapel, such as the; rammed earth walls, radial walls, butterfly roof, and extensive use of locally sourced materials.
[ via: archdaily.com ]
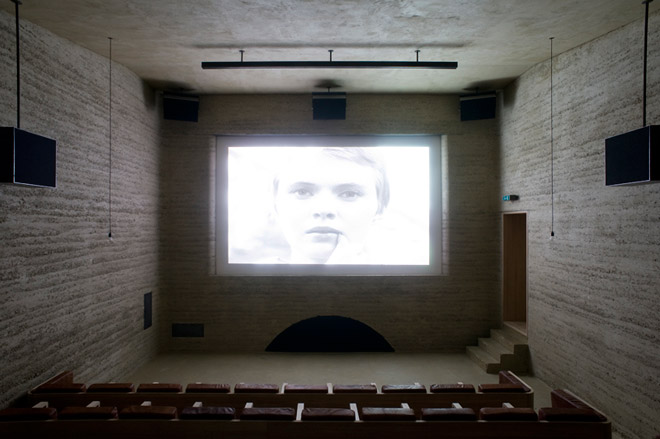

Photography: Bruno Augsburger and Laura Egger
Over two decades ago, the last cinema closed in Ilanz, an Alpine town in the Swiss canton of Graubünden. To satisfy the locals’ cinephile needs, a group of people interested in film and culture formed the Filmclub Ilanz in 1989 and, after staging screenings in makeshift locations (including the town hall), they had a stroke of luck in 2004 in the shape of a 19th century former forge, which had just become vacant. After several years of screenings, they decided to revamp the space, with the help of fellow club members Capaul & Blumenthal Architects, to create a fully fledged cinema, which opened last September.
The ETH Zurich graduates have retained the raw character of the building, creating a cosy screening room and bar on a shoestring. Using local clay and a rammed earth construction method – a sustainable, low-tech building technique with sound-proofing benefits – the project was completed with the help of members of the Filmclub, who also conveniently included a rammed-earth specialist and a stonemason. Seating in the auditorium is padded by sheep-skin covered cushions stuffed by Filmclub members. Meanwhile, paint on the walls of the bar and stage area has been stripped back to reveal the original lime plasterwork of the building and floors are kept bare. The bar itself can be lifted by a manual forklift to make space for a dance floor when there are concerts – just one part of the Cinema Sil Plaz’s rich programme of events.
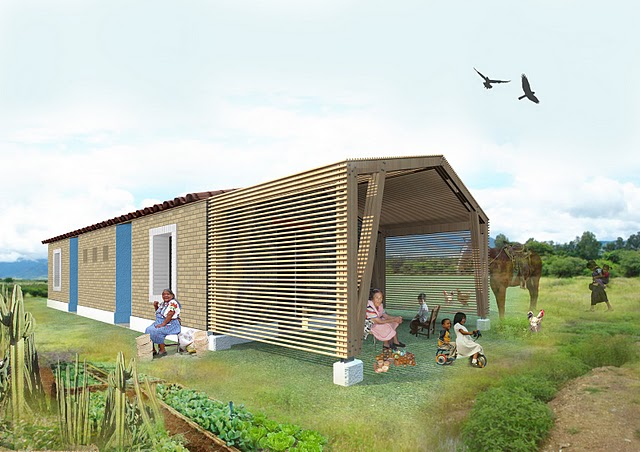

Adobe for Women is a non-profit association, founded in 2011, whose goal is the recovery and education of earth construction techniques; this is our contribution to a more human and sustainable use of space and the planet’s resources. The goal of this Project is to build 20 sustainable houses in the indigenous village of San Juan Mixtepec, in the southern Mexican state of Oaxaca.
The houses are intended for 20 women in difficult circumstances who will participate in the building process. They will slowly appropriate their future home and simultaneously re find their self esteem, work abilities and hope that will transform the spaces into safe, caring places for their families.
The houses are energy efficient and built with local materials such as adobe and bamboo.
The Juana Briones House, a rare example of encajonado construction, parts of which were built in 1844, has been completely torn down by property owner Jaim Nulman, who fought off historic preservationists, latino activists, and descendants of Briones for years. Feminists joined in the struggle for the home’s preservation as well. Jeanne McDonnell, biographer of Juana Briones, stated that historic buildings associated with women are more likely to be demolished than those associated with men.
In a world increasingly concerned with questions of energy production and raw material shortages, this project by Markus Kayser explores the potential of desert manufacturing, where energy and material occur in abundance.
In this experiment sunlight and sand are used as raw energy and material to produce glass objects using a 3D printing process, that combines natural energy and material with high-tech production technology. Solar-sintering aims to raise questions about the future of manufacturing and triggers dreams of the full utilisation of the production potential of the world’s most efficient energy resource – the sun. Whilst not providing definitive answers, this experiment aims to provide a point of departure for fresh thinking.

After weeks of enduring the ash brought on by Chile’s Puyehue volcano, one Argentine woman has decided to transform the grey sediment into something useful. Maria Irma Mansilla used the sediment and sand spewed by the volcano to create bricks. She hopes she and her neighbours will be able to produce them on a large scale to build homes for the poor. Watch

The Sra Pou vocational school in Sra Pou, Oudong, Cambodia by Finish architects Rudanko + Kankkunen is constructed of hand-dried blocks of the surrounding soil. The school serves as a business training centre and public hall.

The soil block walls repeat the warm red shade of the surrounding earth. They are laid out with small holes, so that indirect sunlight and gentle wind come in to cool the spaces – and at night, the school glows like a lantern through these small openings. The whole community space is open, providing comfortable shaded outdoor space. The colorful handicraft doors are visible from far away and welcome visitors coming along the main road.

The 200m2 building cost $15,000 and was constructed by members of the community.
More at dezeen.com

From FastCOdesign: Diébédo Francis Kéré Imbues Mud With Poetry, And Gives Africans A Future
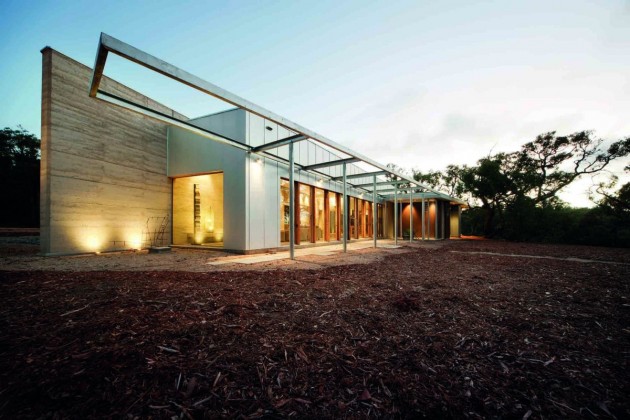

The Hinterland House by http://www.morrispartnership.com.au/ is a rammed earth house designed to be in harmony with the Australian bush. No fences, screens or garden areas were incorporated to insure as little disturbance as possible to surrounding inhabitants. The local animal and plant life can continue to roam as freely as before the structure was built.
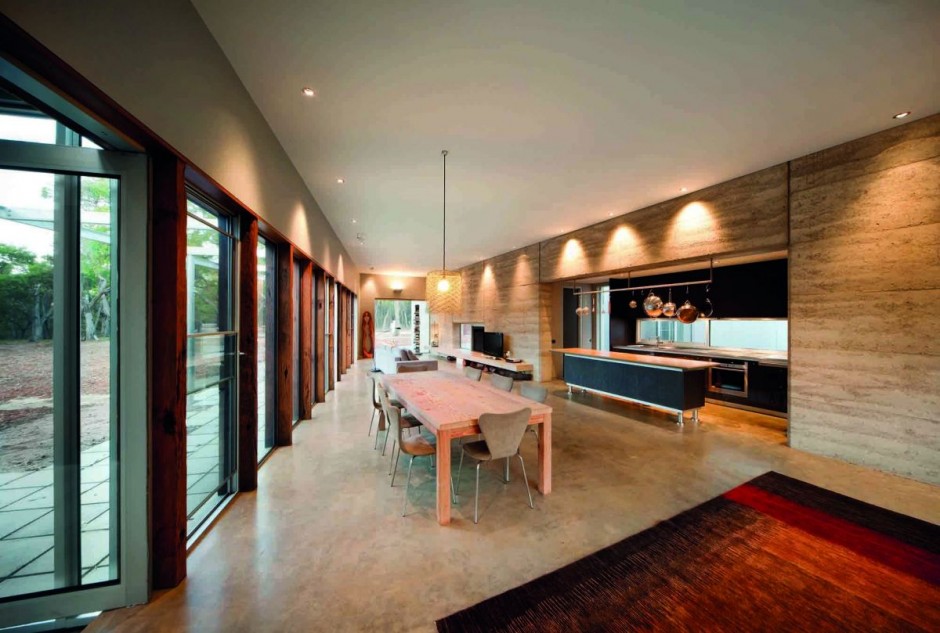

Along with rammed earth, the material palette includes spotted gum, rough recycled timber, concrete floors, corten steel and zincalume. Building environmental features include the earthen thermal mass, double glazing, shading and cross ventilation that mitigates against the need for air conditioning. Sustainability solutions include the use of worm farm waste treatment, solar heating and hot water, and the cellar pantry drawing cooled air through an underground chamber.
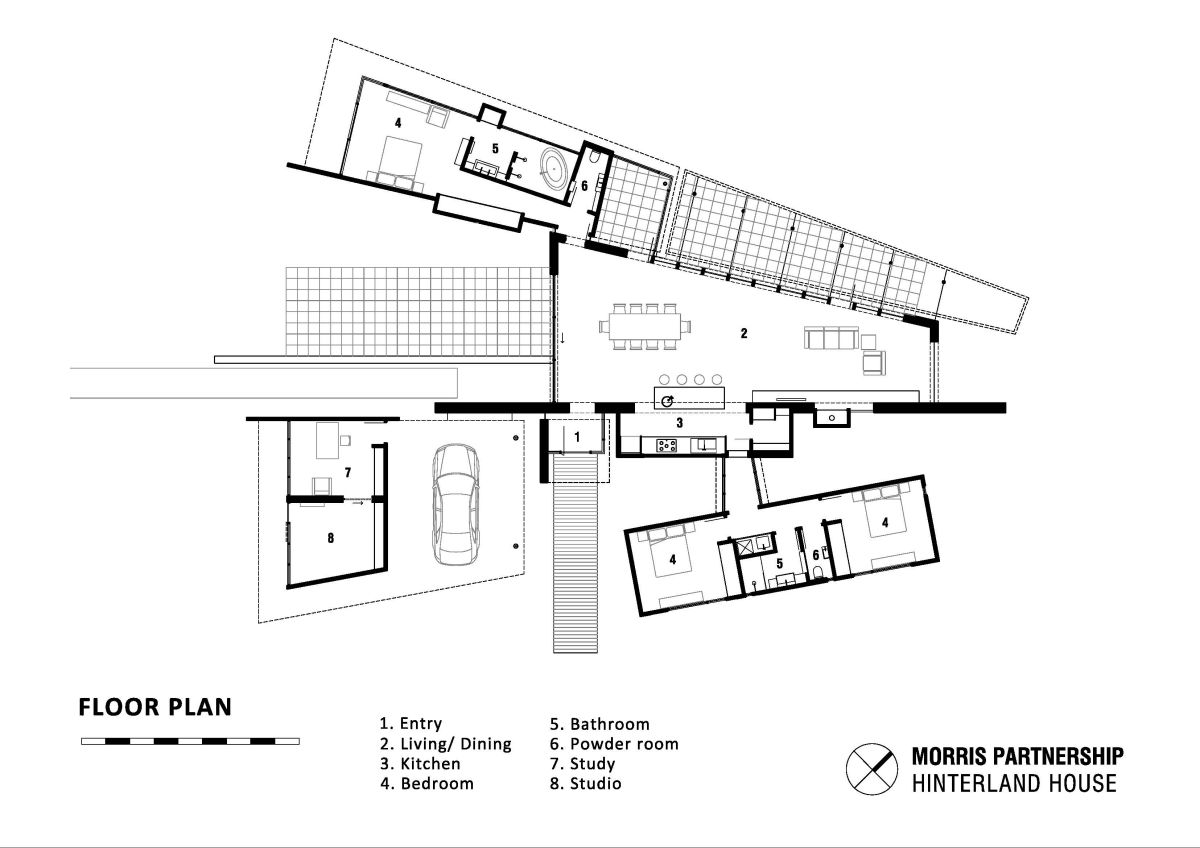
The Hinterland House program includes:
· Living/dining/kitchen core
· Clients’ separate bedroom suite
· Separate studio & study
· Separate guest accommodation