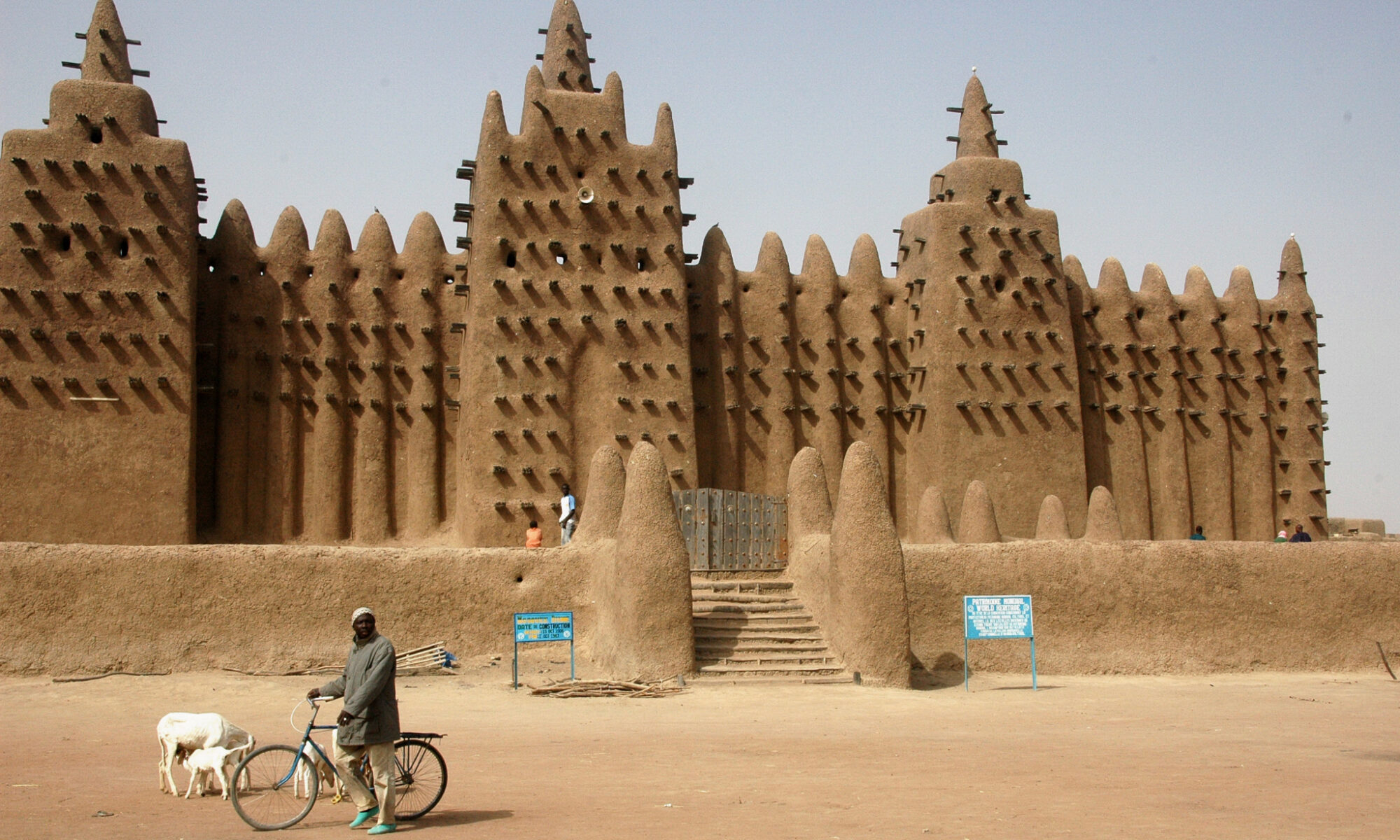
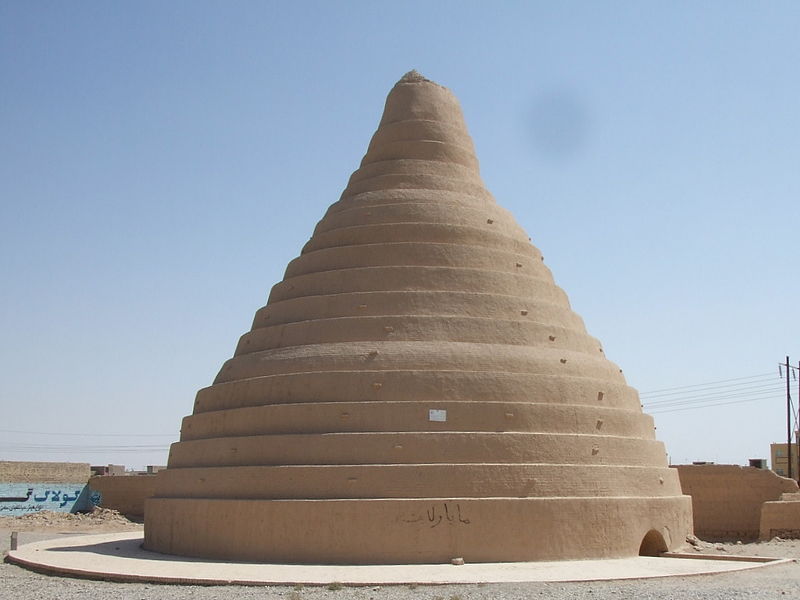
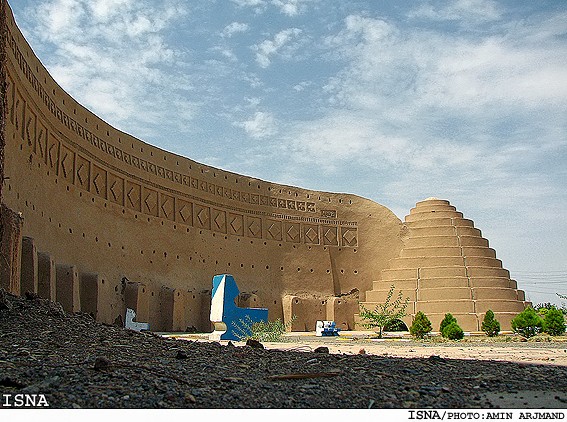
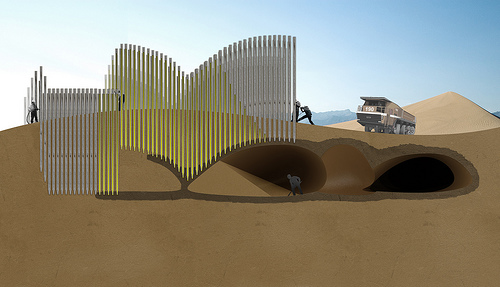
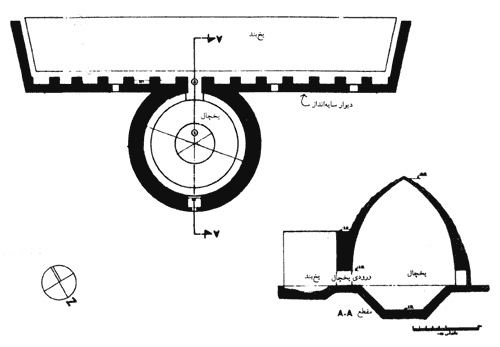
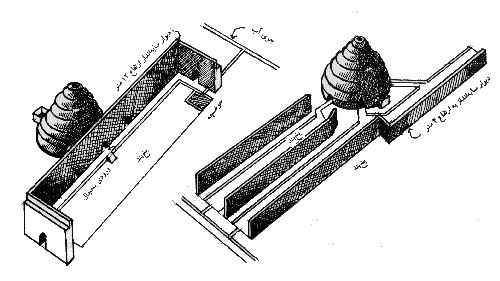
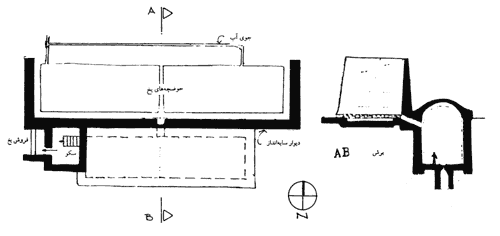
Earth Architecture, the best-selling book born from this blog, has received several reviews. Buy Earth Architecture and read what others are talking about:
“…an excellent and thoughtful survey of earthen structures across the world and throughout building history.”—Geoff Manaugh, BLDGBLOG
“…an excellent book that outlines the history and explores in-depth contemporary uses of earth in architecture….a powerful corrective to those commentators that view buildings made of earth, or the matter that constitutes earth buildings (mud, sand, gravel, soils), as primitive, poor, or crude.”—David Gissen, Architectural Historian
“Earth Architecture compellingly underscores the need for us to rethink how we can build sustainably by using old techniques in new ways.”—Azure Magazine
written in “simple, descriptive prose, each project is traced in a way that creates an anthology and motivates the reader to further study and research. The book is rich in content and draws in other authors, architects, historical buildings and periods.”—Building Design
“…a satisfying survey both for the professional “mudder” and for those who want a quick scholarly survey of earthen buildings from all over.”—Architects Newspaper
A “Must Have”—WorldArchitectureNews.com
“…contains a wide range of modern earthen residences from the simple to the stunningly opulent. A beautiful book for earth-based building enthusiasts.”—GreenMuze.com
“…brings to the fore earth architecture and its positive impact on architectural design….an important addition to any architect’s library for its important subject matter and the quality of projects included.”—A Daily Dose of Architecture.com
Earth Architecture “charts a grand history of architectural beauty crafted from one of the humblest of building materials”.—The Age, Melbourne
Buy Earth Architecture if you live in the following countries::
[ U.S. | Japan | Germany
| Germany | U.K.
| U.K. | France
| France | Canada
| Canada | Australia ]
| Australia ]