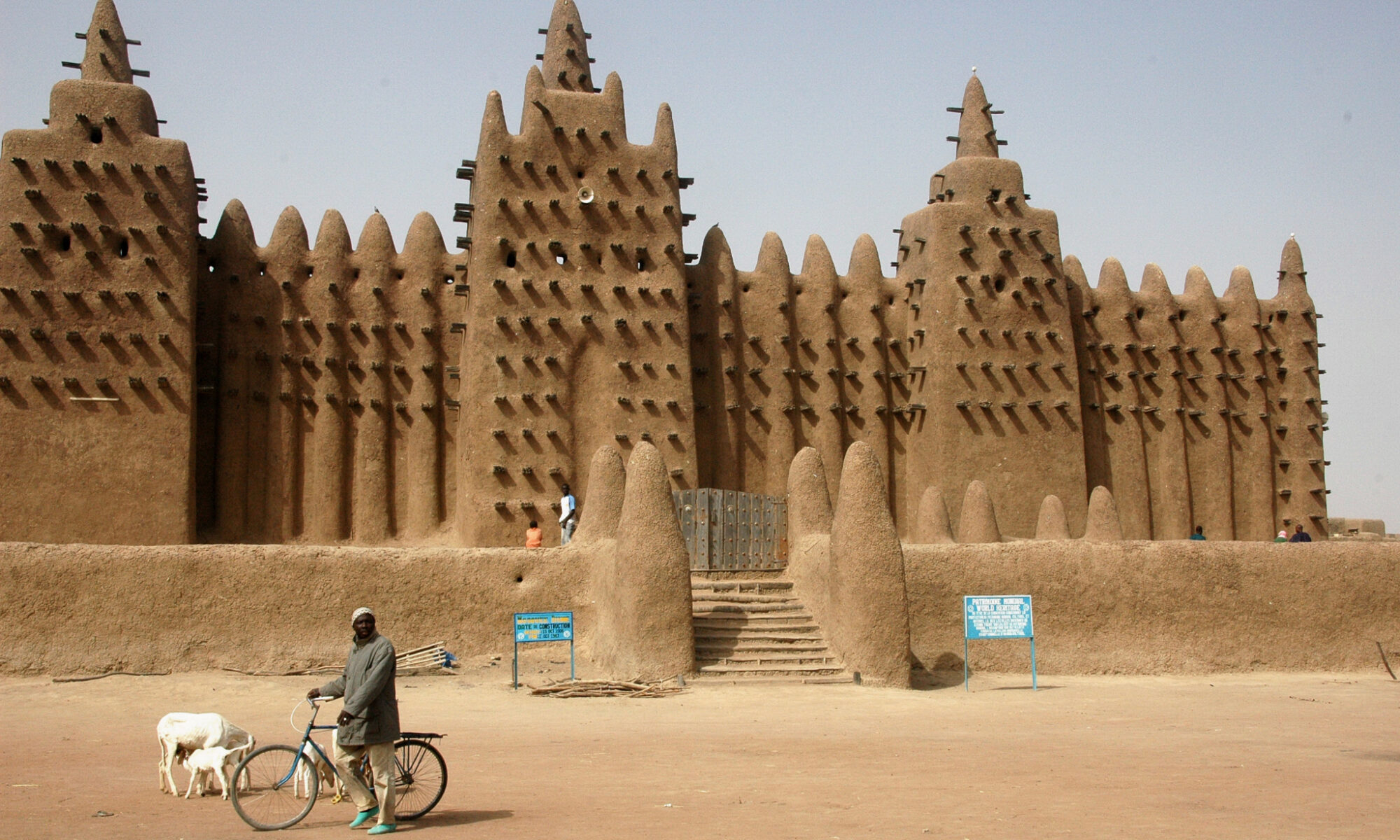
The Association La Voute Nubienne is involved in a fascinating project with friends in France and Burkina Faso in the construction of vaulted earth roofed houses. The Nubian vault is an ancient architectural technique, traditionally used in Sudan and central Asia, but until now unknown in West Africa, which can accelerate appropriate house-building in the Sahel. The technique uses basic, readily available, ecologically sound, local materials (earth, water, rocks…) and simple, easily learned procedures. The major cost element is labour, so cash stays in the local economy. In Burkina Faso, Mali, and Togo, trained VN builders are becoming independent entrepreneurs. Lots of photos, and a video, of AVN houses and other buildings (a church, a mosque, guest-houses…) can be see on their website.
Last month, they put in a bid to Ashoka (a global foundation promoting social entrepreneurship) for their Changemakers competition on “How to Provide Affordable Housing.”, and we have just been informed that we are amongst the 13 finalists shortlisted by a panel of five distinguished judges. Of these 13 finalists, 3 are to be chosen for the competition prizes by online voting, which must be done by October 16th. I’m writing to ask you whether you might spare a bit of time to have a look at this shortlist, and to vote for them (and for two other of the short-listed projects).
If they win one of the three prizes, the money will be used to finance the training of more AVN apprentices during the coming winter building season in Burkina Faso. And I can assure you that this is a very worthwhile, sustainable project : Nazira and I stayed in a VN guest-house in Boromo, Burkina Faso, last January, and can vouch for the quality and comfort of the buildings.
Each voter is required to cast votes for three of the projects – otherwise your vote is rendered invalid. (Ashoka say this is a good way of ensuring fair play, and has worked well in past competitions). The deadline for voting is October 16, 2006. The Changemakers Innovation Award winners will be announced on October 17, 2006.
This is where to go to see the short-list and to vote online : http://www.changemakers.net/journal/300606/